Author: Olga Sergeevna Shiltsova, practicing veterinarian, diploma from St. Petersburg State Academy of Veterinary Medicine in 2011
The condition of the skin and coat is the main indicator of the health of our pets. Long before other signs of disease appear, owners notice the appearance of dandruff, dull fur or scratching. If we talk about skin damage, cats suffer from them much more often than dogs - due to their own sharp claws and rough horny tongue. Scratching on the skin is a clear sign of itching in a cat, even if the pet does not itch in front of its owners and tries to maintain a calm appearance.
Inflammation of the skin, areas of baldness, itching are reasons to consult a veterinary dermatologist. The doctor will identify the cause and prescribe medications for scratching in the cat based on the diagnosis.
Inner ear diseases
These ailments are the most serious. They are difficult to identify, it is difficult to even imagine how to treat ear diseases in cats, since the picture of the course can be blurred, the shape can easily change, affecting either the outer, then the middle and inner zone of the auricle.
Mostly otitis media occurs. This is an inflammatory process that has various causes. 3 types are classified: external, middle, internal otitis. With external inflammation, the symptoms are similar to otodectosis - redness, wax in the ears, and various irritations. But in this case, the pet does not itch as often.
If the detection of the disease is delayed, hair may fall out and pus may appear. Causes of infection:
- Injury or splinter;
- Hypothermia;
- Fungi;
- Sulfur plugs;
- Allergy;
- Infections.
Various microorganisms and viruses can lead to inflammatory processes. Otitis media forms if the auditory tube is affected. Air ventilation is impaired. This type is very rare.
Self-treatment is strictly contraindicated. The disease must be treated by a veterinarian, since with the wrong approach there is a very high risk of complications.
Diagnostic measures
The animal's hearing organs are subject to a thorough examination by a doctor.
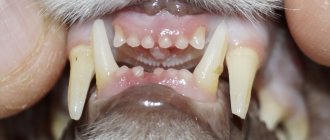
To find out why the ear turns black, the veterinarian performs an external examination. A specific crust, scratching and greasy black discharge help in making a diagnosis. To confirm otodectosis, plaque scraping and examination under a microscope are performed. The procedure takes little time, is painless and non-traumatic. An otoscopy is also performed to find out how much the inner ear is affected.
Symptoms of ear disease
A healthy individual has a pink auricle, its surface is dry, and there is no pungent odor.
The owner should be wary of the anxiety of his four-legged friend. The first signs of ear disease in cats:
- Tilts head to one side;
- Frequent scratching;
- The pet refuses to eat;
- Sharp shaking of the head;
- Swelling is noticeable.
Behavior can be aggressive when trying to look into the ear, or vice versa lethargic. Discharge of different colors or smells may appear, the color of the skin may change, peeling on the inside and dermatitis on the outside may occur.
When the base of the ear is pressed slightly, squelching sounds occur. Such phenomena should not be ignored. The photo shows ear diseases in cats, and we see how hard it is for our pets. In these cases, you need to contact the clinic, specialists will provide the necessary assistance.
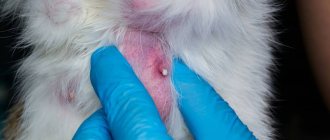
Eczema
With eczema, a cat develops a red spot on its ear as a result of water, chemicals, or a foreign object getting into it. This may also be caused by:
- External irritants (collar rubbing, contact with rough fabric, etc.);
- Allergic reaction of the immune system to individually intolerable components (for example, food);
- Fungi, bacteria, fleas and other parasites;
- Irritants (shampoos, dyes, household chemicals, etc.));
- Seborrhea (scruff);
- Chronic stress;
- Diseases of internal systems and organs (gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidneys, etc.);
- Hormonal disorder.
Eczema can be dry or weepy. The first form is characterized by the absence of infection in the affected areas. The surface epithelium is subject to keratinization, covered with dry scales and tuberosity. The second form is caused by fungi, viruses and bacteria of a pyogenic nature. With weeping eczema, the blisters open on their own and the tissue adjacent to the lesion softens and continuously releases exudate. Eczema enters the chronic stage 3-6 weeks after the start of its development. It is characterized by absolute dry skin and atrophy of hair follicles.
Treatment of ear diseases
To make a diagnosis, it is necessary not only to see the picture of the patient’s clinic, but also to take into account various tissue tests.
The doctor will prescribe treatment depending on the sum of all indicators.
- These can be antimicrobial, antiviral, antiallergic drugs, antibiotics and homeopathic remedies.
- The treatment process can be adjusted, especially with regard to fungal infections and mites.
- For hematomas and neoplasms, the help of a surgeon will be required.
Self-medication can only complicate the process. It is necessary to remember not only about the complications, but also about the harm that can be caused to your little friend when using inappropriate medications.
Hematoma
One form of blood blister can occur in the ears of cats. It appears between the layers of the ear due to scratching of the ear. Blood from damaged vessels forms clots. They are usually removed by surgery or careful treatment with special ointments. The course of their application to the affected area is a couple of weeks. Often a hematoma is formed due to mechanical damage. If you are free-ranging with your pet, you should always be on guard.
An animal can seriously damage not only the ear, but also other organs, for example, during a fight with relatives or dogs, when falling from a great height, or after being hit by a vehicle. However, sometimes a hematoma is formed due to existing diseases, such as otitis media, fungal infections of the ear, the already mentioned otodectosis and others. Infectious and parasitic diseases cause a cat to constantly scratch its skin, which leads to self-harm.
© shutterstock
Preventive measures
As a preventive measure, you need to regularly clean your animal’s ears. To do this, you must use products prescribed by your veterinarian. Cleaning should not injure the hearing organs; it must be done very carefully.
It is necessary to periodically check and examine your tailed friend, and consult a clinic when the first signs of various ailments appear.
Diagnostics
A preliminary diagnosis can only be made based on the results of the examination, since the diseases have characteristic clinical signs described above. Additional studies are required to confirm the diagnosis. To exclude the presence of a bacterial or fungal infection, a cytological examination of skin smears is performed. Also, thanks to it, you can see the cells that appear in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune disease is confirmed using skin histology. Using scrapings, in most cases it is possible to detect skin mites, but the Demodex gatoi mite is very rarely found in scrapings, and this disease is not easy to diagnose. Several methods can be used to diagnose lichen. First, the animal is examined under a fluorescent lamp - this method makes it possible to detect lichen in 50% of cases, since not all types of this infection will glow under the lamp. Then trichoscopy can be performed, thanks to which you can see the hairs destroyed by fungal spores. A more accurate diagnosis is to inoculate hairs in special growth media. Fungi in such environments can grow for a long time, up to 3-4 weeks, but the accuracy of this diagnosis is at least 95%.
Most often, identifying an allergen is not an easy task; there are no special tests for this. First, using scrapings, cultures, etc., it is necessary to exclude all possible differential diagnoses, which will be suggested by the doctor. If allergy remains the most likely diagnosis, the stage of excluding possible allergens will begin. First of all, fleas are excluded, the animal and the room where it lives are treated. A special elimination diet may then be prescribed to rule out food allergies. If the allergen is not identified, a diagnosis of “non-food allergy” or “atopy” is made.
Photo of medication for treating cat ears
Skin tumors
Tumors that appear on a cat’s head differ in size, shape and origin:
- Lipoma. A fatty benign tumor can increase in size. There is no metastasis. It occurs in older cats on any part of the body.
- Abscess. Appears under a cat's fur after an insect bite or an unsuccessful injection. Causes pain and fever.
- Mite under the skin. Represented by a small tubercle. Does not cause pain or discomfort to the animal.
Important! Sometimes bumps in cats occur as a result of injury and go away on their own.
History taking
Before diagnosing diseases in cats, a medical history is taken. It involves studying several factors.
Age and breed
In kittens up to one year old, itching and rashes all over the body can be caused by dermatophytosis or skin parasites. Adults under 4 years of age are most susceptible to allergies. And in older cats, sores are often associated with skin tumors.
Some cat breeds are predisposed to skin diseases. In Sphynxes these are allergies, in Persians - idiopathic dermatitis and dermatophytosis.
Lifestyle
Keeping a large number of cats, visiting exhibitions, access to the outdoors - these and other factors increase the risk of infection with skin parasites, fungal, viral diseases and other cat diseases.
Seasonality
Allergies to plants and pollen, tick and mosquito bites - these causes of itching and sores are seasonal.
Lichen
This disease is already dangerous for humans, so if spots with round rings around them appear on the ears, and then they spread to other parts of the animal’s body, cutting off large areas of fur, there can be no doubt – this is ringworm. A rather unpleasant skin disease of fungal origin is transmitted to humans, so the following precautions must be observed :
- carry out a thorough cleaning of the apartment using disinfectants;
- disinfection is carried out only with rubber gloves;
- the cat should be isolated during the illness.
© shutterstock
The veterinarian prescribes special medications that have an antifungal effect, their use leads to the fact that the disease disappears, and the danger for cats of becoming bald is completely eliminated. It is also important that a person is safe when treating lichen, since it can also appear in people.
Clinical manifestations
With parasitic dermatitis, the four-legged pet becomes nervous, refuses to eat, and suffers from incessant itching around the ears and tail. He constantly itches, licks himself and even bites himself. The skin becomes covered with rashes, red spots, and peels. Weeping sores and crusts form on the back, neck, chest and behind the ears. Fleas and lice eaters can be identified during an external examination.
If the dermatitis was caused by a subcutaneous mite, then skin lesions are also observed on the limbs and eyelids. It is not possible to detect the parasite with the naked eye.
The cat's appearance deteriorates. The coat loses its shine, becomes dry, brittle, and alopecia is possible.
Allergic dermatitis is characterized by the appearance of blisters, pustules, swelling, and redness of the skin, especially in the abdomen and groin area. When touching the inflamed areas, the animal experiences pain.
Histamine, which the body produces in response to the allergenic component, causes severe itching. The cat is continuously coughing and sneezing. The eyes become red and watery.
Atopic dermatitis occurs in cats between 10 months and 3 years of age. Allergens include plant pollen, dust, components contained in perfume compositions, and much more.
The inflammatory reaction in contact dermatitis is localized in the place where the skin comes into contact with a dangerous substance. Various acids, alkalis, pastes, and creams can act as the “aggressor”. The cat is bothered by itching on the paw pads, in the abdomen, neck, chin, and anus.
Purulent dermatitis is characterized by a chronic course. According to the clinical symptoms of the inflammatory process, it can be wet and dry. In the first case, erosions form on the damaged skin, in the second - scabs and crusts.
Superficial dermatitis manifests itself in the form of small redness and, as a rule, goes away on its own.
Special cases
There are also special cases that we have already indirectly mentioned above. We are talking about some cat breeds that, as a result of many centuries of selection, have acquired some specific characteristics. In particular, sphinxes have ears that are so “original” that they have no ability for natural self-cleaning at all.
In addition, this breed has another feature: their ears produce particularly large amounts of wax. Normally, it protects the ears from pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microflora, as well as foreign objects, but sphinxes have too much of it. And therefore, heavy plaque inside the hearing organs is commonplace for such cats.
If plaque is only in one ear
In cases where there is plaque in only one ear, we can talk about:
- Or is it an individual feature of a cat that synthesizes more sulfur in one ear (this happens, and is not so rare).
- Or, what is much more likely, one ear is already affected by a tick, or an inflammatory process of a different etiology has already developed there. You shouldn’t expect miracles: over time (more precisely, very soon), parasites or harmful bacteria will end up in the second ear. Moreover, if we are talking about otodectosis, both ears will still have to be treated.
What does a strong smell from the ears mean?
Nothing good. Normally, cats' ears, although they do not smell lavender, still do not cause gag reflexes.
Therefore, a pungent odor may appear in the following cases:
- Fungal infections (we have already written that the smell is very specific).
- Purulent inflammation.
- Advanced forms of otodectosis.