The appearance of subcutaneous lumps on the body of a pet is an alarming sign that requires mandatory diagnosis. The wide variety of possible causes precludes any attempt at self-treatment. An incorrectly selected technique can harm the pet and worsen its well-being.
Despite the danger of possible consequences, do not panic. Many neoplasms are benign. For an accurate result, a thorough examination at a veterinary clinic will be required.
Abscesses
An abscess is a pus-filled, swollen spot on the skin that sometimes forms at the site of a cat bite or scratch. They are often red and painful, so your cat may shy away from your touch.
Cats with an abscess may appear more tired than usual and may not show much interest in eating. A warm compress may give them relief.
To treat an abscess, your veterinarian may prescribe an antibiotic and an anti-inflammatory medication for your cat. They may also trim the hair around the bump to keep the wound clean. If the abscess is deep, your cat may need surgery.
Treatment
Depending on the type of cone, the treatment is different:
- The wen opens on its own when it is “ripe”. A viscous substance is released from the hole after opening. You need to carefully squeeze out the contents and treat the wound with an antiseptic.
- The abscess is opened surgically and preferably under sterile conditions. If the inflammation is not opened, the abscess can burst and lead to infection of the entire animal’s body.
- In case of purulent lymphadenitis, the lump must be opened surgically and the wound must be sanitized. In the absence of pus, vitamin therapy is carried out, and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. It is imperative to establish the cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes and first of all fight the cause of the underlying disease (for example, sore throat).
- Benign tumors and cysts are removed surgically if they cause discomfort and worsen the animal’s life. If the cyst is small or if the animal's condition does not allow surgery, the growth and development of the cysts is monitored.
- The tumor goes away on its own after vaccination; no special methods or treatments are required.
- Oncological tumors are treated only by surgery. Moreover, during the operation, not only the tumor, but also part of the healthy tissue is cut out in order to avoid further development of the tumor. Chemotherapy courses are being carried out.
Tumors
Fatty tumors, called lipomas, can appear anywhere on a cat's body. They are not cancerous and do not need to be removed unless they interfere with your cat's ability to move around normally. They are more common in older or overweight cats.
To check for swelling, your veterinarian will take a sample with a needle. If it's just a fatty tumor, doctors may advise you to do nothing and watch the tumor. If the lump changes or becomes larger, your veterinarian may suggest surgery.
Mast cell tumors can also appear on a cat's skin, usually on the head or neck. They may be itchy or red. About 10% of these tumors are malignant.
Fibrosarcomas are aggressive cancers that can appear anywhere in the body. In rare cases, they occur as a side effect of any injection given.
If your cat develops a lump at the site of a recent vaccination, notify your veterinarian. They will want to examine your cat right away. These tumors usually appear long after vaccination.
One of the most common types of cancer in cats is mammary cancer, or mammary tumors. They appear on the cat's underside near the nipples and often go unnoticed until they become large.
Initially, these tumors may feel like IV granules. About 85% of these tumors are cancerous, so don't delay taking your cat to the vet if you notice anything unusual.
If you spay your cat before her first heat, you will reduce the risk of breast cancer by about 90%.
If your cat has any type of cancer, she will likely need surgery to remove the tumor and the tissue around it. Your veterinarian may refer you to a veterinary oncologist who treats animals with cancer.
For breast cancer, the best treatment may be to remove the entire breast. In some cases, your doctor may recommend radiation therapy or chemotherapy after surgery.
Types of bumps under the skin of a cat
Cones can have a different nature, depending on the animal’s predisposition to a particular disease.
Lipoma (wen)
At first, a small formation appears, which gradually grows and can grow to the size of a chicken egg. The cause of lipoma is improper distribution of fat after clogged pores. Lipoma is a benign neoplasm that does not metastasize and does not cause discomfort. The exception is if the lipoma occurs on the back or neck. The lipoma does not hurt even when pressed, it does not affect life processes: the appetite is preserved, the animal’s normal behavior, the temperature is normal.
In older animals, the appearance of lipomas may indicate the onset of cancer. You should definitely have your cat examined by a veterinarian.
Abscess
An abscess appears at the site of a bruise, any internal injuries, or in case of an incorrect injection.
The tumor appears approximately on the 3rd day after injury, gradually growing.
Unlike a lipoma, an abscess is a painful condition, accompanied by an increase in temperature and depression of the pet’s condition.
The abscess is firm to the touch, but not hard. You can feel accumulated pus inside. If the abscess is not completely healed, pus is released into the hole when pressed.
Lymphadenitis
Inflammation of the lymph nodes. The lump is extremely painful even with slight pressure. The animal's condition is depressed, the temperature is elevated, and the appetite is reduced.
Cyst
A cyst is a benign tumor. A cyst is a lump filled with fluid from the inside. This tumor grows slowly and does not affect the cat’s condition; the cyst is not painful.
Tumor as a reaction to vaccination
Usually there is a slight swelling, a little painful, accompanied by redness.
Oncology
The most terrible type of neoplasm. This is what the owner thinks about when he feels a lump on his pet’s body. Cancer spreads very quickly and metastasizes throughout the body. Inevitably leads to the death of the animal, but in the first stages of the disease it often does not manifest itself.
What are the causes of swelling?
Traumatic injuries
Cats love to rub their faces against various objects, leaving their marks on them. Therefore, your pet may accidentally get hurt or get a splinter. A foreign body provokes inflammation, which causes swelling. A pet can hit its face during outdoor games and a hematoma occurs, in which bleeding occurs under the skin. Symptoms:
- painful swelling;
- unexpressed asymmetry of the muzzle;
- bloody crust if the skin is damaged;
- purulent discharge when the inflammatory process was not detected in a timely manner and the wound became infected.
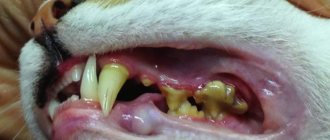
Gum inflammation
Gingivitis is accompanied by reddening of the gums and bad breath from the pet.
Gingivitis covers the teeth and mucous membranes, spreading to the ligaments and bone structures of the jaw. The main reasons for the development of the disease are a lack of vitamins A and C, the introduction of bones into the diet that injure the gums, the formation of tartar, severe viral diseases, and malocclusion when the teeth regularly damage the mucous membranes. Signs:
- profuse drooling;
- putrid odor from the mouth;
- redness and swelling;
- decreased appetite;
- loss of body weight.
Eosinophilic granuloma
Most often it occurs on the lips due to allergies of various etiologies. It appears as an ulcerative tumor or plaque and appears predominantly on one side of the muzzle. Unfavorable factors for the development of granuloma are helminthic infestation, skin parasites, food components, household chemicals, some types of indoor plants, fungus or mold in the room. Manifestation:
- the appearance of dense nodules and ulcers on the lip;
- swelling;
- absence of pain;
- decreased food and water intake, which causes the cat to lose weight and show signs of dehydration.
Odontogenic osteomyelitis
If the cat refuses to eat and looks lethargic, this indicates the development of the disease.
The causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus. Inflammation affects all bone structures and bone marrow of the lower jaw. The main factor in the development of osteomyelitis is considered to be advanced gingivitis, abscess, periodontal disease, wounds through which infection entered, and incorrectly performed dental procedures. In advanced cases, the cat will not live long. Symptoms:
- local and general hyperthermia;
- lethargy, refusal to play and eat;
- increased thirst;
- the appearance of a fistula on the jaw, from which pus is released;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- enlargement of local lymph nodes;
- redness, swelling;
- the appearance of areas of necrosis.
Neoplasms
According to veterinarian statistics, tumors of the mandibular joint and oral structures in cats account for 10% of the total number of pathological formations.
A dangerous manifestation in an animal is a salivary gland cyst, as it can degenerate into oncology.
If your cat has a lump on his chin, it could be a benign or malignant tumor. Among non-oncological pathological formations, a cyst of the salivary glands - mucocele - is most often diagnosed. Due to injuries, a cavity is formed in which saliva accumulates. It is manifested by slight swelling, there is no pain. Mucocele is dangerous due to degeneration into cancer.
Among malignant neoplasms, the lower jaw is affected by sarcoma or squamous cell carcinoma, which are characterized by an aggressive course and rapid formation of metastases. Oncology occurs due to a failure of the cell cycle, when cells begin to rapidly divide and form a compaction. Most often, cancer is provoked by the owner’s smoking in the presence of a cat, decreased immunity, and chronic inflammation of the jaw bone. Cats with cancer live 3-12 months. A malignant tumor of the lower jaw manifests itself as follows:
- pronounced compaction that increases in size;
- salivation;
- the appearance of blood clots;
- sudden weight loss;
- strong pain;
- general deterioration of health.
Kinds
Conventionally, all neoplasms can be divided into two groups: benign and malignant. The first include:
Abscess. It looks like a lump filled with pus inside. It may appear as a result of a bruise, a fall, an unsuccessful injection or other damage to the skin. There are superficial and deep abscesses. The first is formed in the upper subcutaneous layer; it is easy to detect by swelling of the tissues and their red color. Deep affects internal organs and is not visually diagnosed.
Quite often, dogs experience inflammation of the paraanal glands, which leads to the appearance of lumps around the anus. When the problem is aggravated by infection, the area becomes very swollen, accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
Papillomas and warts. Frequent companions of smooth-haired dogs. The disease is transmitted through contact with a carrier of the virus. Formations can appear either singly or crowded. They hang in “clusters” on individual parts of the body, having a branched structure and dark coloring. Loose and soft to the touch.
As a rule, papillomas appear in the mucous membranes (mouth, eyes), as well as on the abdomen, groin areas and armpits. Despite their unaesthetic appearance, hanging “balls” may not cause any trouble to the animal, but if they begin to change color or bleed, then you should immediately see a veterinarian.
Hematoma. The cause may be vascular ruptures and, as a result, hemorrhage into adjacent tissues. The accumulation of excess fluid leads to the formation of lumps, which can either go away on their own or be opened surgically.
Most often, hematomas appear as a result of bruises or blows, as well as various medical procedures. The more damaged the vessel is, the larger the lump grows. The dog may react to the problem with an increase in body temperature, poor appetite, nervousness, or, conversely, apathy. Sometimes there may be enlargement of the lymph nodes.
Cyst. It is always localized in the superficial layer of the skin, has a round shape and usually does not “respond” with pain when pressed. The size can vary between 2-5 cm in diameter, it feels loose and soft to the touch. A cyst-shaped ball can be found under the skin anywhere due to blockage of the gland ducts. Depending on its location, the cyst may not cause any discomfort to the dog or, on the contrary, interfere with movement, chewing food, lying on its side, etc.
Pyoderma. Predisposition to the disease persists in puppies up to 4 months of age. The bumps appear suddenly and are spontaneous in nature. They quickly spread throughout the body, degenerating into purulent boils. Often they open spontaneously and take the form of fistulas. Accompanied by itching and scabies.
The most vulnerable to pyoderma are dogs of small breeds (Chihuahua, Yorkshire terrier), as well as boxers, sharpeis, and French bulldogs.
A separate category includes insect bites - spiders, wasps, ants, hornets. A severe swelling occurs at the site of the bite, which is painful, itchy and itchy. Due to the fact that the dog scratches the sore spot with its paws, the lump may not heal for a long time and turn into an open wound.
The most unfavorable development of the situation is the development of benign formations into malignant ones. It is impossible to predict the speed of the process, everything is individual. The bumps may not bother the dog for years, and then begin to change, or they can actively grow and immediately serve as a source for the spread of metastases throughout the body.
Older animals are at greater risk of developing sarcoma, but fibrosarcomas can affect small puppies under 6 months of age. Visually identifying a malignant tumor is possible only in the later stages.
Oncological formations
Oral cancer is a rare occurrence. According to statistics, in three cats out of a hundred, cancer causes the formation of a malignant lump in the area where the whiskers grow. Therefore, if you notice a tumor on the face, immediately contact a veterinary clinic.
The cause of a malignant tumor can be a pet’s poor diet, based only on canned food. Smoking by the owner in the presence of the animal. Most often, squamous cell carcinoma or fibrosarcoma . Cancer treatment is carried out outside the home. The sooner the owner contacts the clinic for a diagnosis, the greater the animal’s chances of survival. As a rule, surgical removal of a tumor on the cheek is prescribed. To prevent metastases from appearing, doctors administer chemotherapy. But if the owner missed time, did not pay attention to the symptoms and started the disease, it will not be possible to cure the cancerous tumor.
Opening an abscess on the gum
The abscess is always opened. This reduces the risk of spontaneous opening, which can cause complications. The flux is opened under local anesthesia. If the patient has panic or other indications, the doctor may choose a different method of anesthesia.
A small incision is made on the anesthetized gum in the area of the gumboil, no more than 2 cm in length. After the dissection, the doctor completely cleans and sterilizes the purulent cavity and treats it with antiseptics. A crust should not be allowed to form in the area of the incision, as it will interfere with the outflow of ichor and purulent contents. To do this, a drainage is inserted into the incision. After the cavity is cleared of pus, you can begin general treatment, the purpose of which is to eliminate the causes that caused periostitis.
Lump on cat's neck due to thyroid gland
Finally, another explanation for why our cat has a lump on her neck could be an increase in the size of the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck and in some cases can be felt. This increase in volume usually occurs due to a benign tumor and consequently leads to excess secretion of thyroid hormones, which cause hyperthyroidism, which affects the entire body.
An affected cat will exhibit symptoms such as hyperactivity, increased hunger and thirst, but thinning, vomiting, poor hair coat, and other rather nonspecific symptoms. It can be detected with a hormonal test and treated with medications, surgery, or radioactive iodine.
Oral diseases
If a cat has a formation on its face and the eye is festering, it may be due to a dental disease. Problems in the oral cavity can cause enlargement of surrounding tissues.
What diseases can lead to the formation of a swelling on the cheek?
- Flux . This is an infectious disease. Suppuration occurs in the periosteum and in the tooth. A lump with purulent contents forms. If the process is started, it can spread to neighboring tissues. Subsequently, a fistula forms and pus flows out of the resulting hole. If it lasts for a long time, the ears and eyes can fester.
- Gum disease . Oral infections can lead to various inflammations in the gums.
- Stomatitis . A painful ulcer appears in the mouth. Due to swelling and inflammation, the cat will not be able to open its mouth wide and eat.
Each of these diseases is painful. In order not to torment the animal, it is better to give it painkillers. It is necessary to contact a veterinarian as soon as possible. Prolonged illness will lead to tissue necrosis and jaw deformation. The cat will not be able to eat normally and will become very thin.
Rinse
They are used as an additional treatment in order to completely remove pus and ichor from an opened abscess and prevent the infection from spreading to healthy areas. Soda-salt baths and rinsing with antiseptic solutions help make treatment more effective and speed up gum healing. When rinsing, you must adhere to the following rules:
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are used as additional ones. They allow you to quickly cope with the infection and stop the inflammatory process. The following methods can achieve good results:
- Fluctuarization. The inflamed tissues are exposed to low voltage current.
- Electrophoresis with lidase. Electrical current is applied to the tissue, allowing the drug to be effectively distributed.
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy. The method is based on the influence of an electromagnetic field.
- Ultrasound therapy. The effect of ultrasound on infected tissues accelerates their regeneration.
- Laser therapy. Damaged tooth tissue is treated with a laser beam.
Furuncle
This is not just an abscess - inflammation of the epithelium, but a disease (in acute or mild form) caused by decreased immunity and focal damage to the hair follicle. It is purulent and necrotic in nature, caused by white or aureus staphylococcus, and begins with a red tubercle:
Gradually, the sore increases, fills with pus, becomes painful, body temperature rises, apathy and loss of appetite are possible. The lesions affect some or all parts of the body, or isolated ones.
Under the skin, the pus is located, as it were, in a “vessel” that restrains the boundaries of inflammation, and after “ripening” one (or several) gray dots will be visible from above - the rod.
Do not squeeze out the boil! Otherwise, the pus will spill over the adjacent tissues.
The veterinary clinic will do everything you need, and in the case of a chronic form, they will prescribe antibiotics.
Keep a sick animal especially clean by placing disposable diapers on top of the bedding every day. Don't bathe! Trim the fur from the site of inflammation, apply ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky, wipe with alcohol while changing the compress, give an anesthetic. In case of spontaneous opening of the sore, clean it as much as possible from pus (do not press!) and reapply a bandage with ointment, changing it every 4-6 hours until the wound is completely cleansed.
What will be offered at the veterinary center
To determine the characteristics of a tumor in the neck, the doctor:
- conduct a survey;
- examines;
- will do all the necessary tests.
The examination involves feeling the lump. Perhaps, if it is a large abscess, then it will be eliminated immediately by removing the pus and washing the wound.
If additional data is needed for a complete picture, the doctor will refer you for detailed tests and procedures:
- Ultrasound;
- Histo- and cyto-examination;
- Donation of blood and urine.
This will help determine how to further treat and care for the cat. Does he need surgery or specific therapy?
One of the most dangerous and varied in symptoms diseases is skin cancer in cats. 75% of all registered skin tumors in cats are malignant. Depending on the type of tumor cell, treatment, prognosis, and clinical signs vary greatly. In this regard, one of the most important stages of therapy is accurate diagnosis of pathology.