Paul Gray, bass guitarist and one of the founders of the popular band Slipknot, said about cats this way: “They, by their very existence, refute the statement that everything in the world was created for man.” These wayward animals have long become full members of families. And although cats love independence, sometimes they may need help from their owner. Visual acuity is very important in a cat's life, and keratitis affects the eyes. But what to do if a serious illness appears and how to prevent blindness in your pet?
1) What is keratitis 2) Reasons for the development of keratitis in cats 3) Symptoms and consequences of the disease 4) Forms and types of keratitis 5) Diagnosis of keratitis 6) Treatment of keratitis in adults 7) Treatment of keratitis in kittens Preventive measures
Preventive measures
What is keratitis
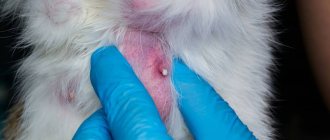
Inflammation of the cornea, or keratitis, is a very common eye disease. A characteristic feature of keratitis in cats is clouding of the cornea, the appearance of ulcers and discharge from the diseased eye. Breeds that are predisposed to the disease include the Siamese, American Smooth-haired, British and Sphynx. The latter is due to the absence of eyelashes and the presence of a large number of folds pressing on the eyelids. The owner needs to pay attention to the cat’s appearance so as not to miss the first signs of poor health.
Why does inflammation occur?
Most non-purulent inflammations of the cornea are of infectious origin. More than 70% of all diagnoses are related to viral activity.
The most common causative agents of keratitis
This type is considered:
- herpes simplex and herpes zoster virus;
- adenoviruses (this variant is more often found in children);
- measles and chickenpox viruses.
If the cornea of the eye is inflamed and purulent exudate is present in the conjunctival sac, the cause of the pathology is a nonspecific or specific bacterial infection. Pathogens in this group include:
- nonspecific bacteria - pneumococci, streptococci and staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli;
- protozoa - Klebsiella and Proteus;
- specific bacteria and protozoa - causative agents of tuberculosis, syphilis, malaria, chlamydia, gonococcus and salmonella.
Inflammations caused by the activity of amoebas of the genus Acanthamoeba are included in a separate group. They cause the most severe damage to the cornea and deep-seated structures of the eye. Such infections are common among people with visual impairments who use contact lenses. They also have a common candidiasis, that is, fungal inflammation of the cornea.
Inflammation does not necessarily require an infectious component.
. In some cases, pathology develops due to:
- autoimmune reactions due to hay fever, taking certain medications or helminthic infestations, rheumatoid arthritis and Sjogren's syndrome;
- intraoperative consequences or complications due to inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eye, lacrimal sac and tubules, sebaceous glands or ciliary follicles;
- endogenous influences - prolonged deficiency of vitamins B, A, C, a general decrease in immunity or chronic systemic diseases accompanied by metabolic disorders (gout, diabetes, etc.).
Also in ophthalmology, inflammation of the cornea due to intense exposure to ultraviolet radiation has been recorded. In this case, we are talking about a separate diagnosis - photokeratitis.
Causes of keratitis in cats
More often, this disease is acquired rather than congenital, and occurs due to infections or mechanical impacts on the cornea (sand, dust, branches, hard objects, etc.), as well as:
- allergic reactions; — chemical or thermal burns of the eyes; - blockage and/or inflammation of the lacrimal glands, resulting in drying out of the conjunctiva and cornea (keratitis can develop in parallel with conjunctivitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyelid - since it fits tightly to the cornea during blinking); — vitamin deficiency; — infections and viruses (herpes, calcivirosis, adenovirus, chlamydia, etc.); - autoimmune diseases.
“Murkoshi” employees recommend examining cats’ vision organs more often to prevent the development of the disease.
Prevention methods
The prognosis of the disease largely depends on how quickly it was diagnosed and how carefully the patient follows the treatment recommendations received from the ophthalmologist. Early stages of keratitis are cured with good effect, the likelihood of relapse is minimal. Severe forms require constant medical supervision and surgical correction to maintain the ability to see.
It is much easier, as ophthalmologists note, not to treat an already formed pathology, but to avoid it. To do this, it is recommended to follow simple preventive measures to prevent the infection from activating or entering the body. Among them:
- avoiding situations in which there is a risk of eye injury;
- the use of special safety glasses if a person’s work involves repairs, construction, or welding;
- careful adherence to hygiene rules when using contact lenses, refusal to wear other people's lenses that may be infected with the herpes virus;
- compliance with precautions when working with substances that can leave a burn on the cornea;
- hardening of the body, which helps increase immunity, preventing the activation of the pathogen in the body;
- protecting yourself from overheating, hypothermia, infections and other unpleasant pathologies that can provoke an exacerbation of herpes.
There is also a vaccine that helps fight the infectious agent. It is recommended to introduce it in early autumn, before the onset of severe cold weather. It is the cold season that often causes exacerbations. Before vaccination, the patient is recommended to take a course of antiviral drugs.
Herpetic keratitis is a disease that develops slowly but steadily. If you ignore it for a long time, you can face significant inconvenience, and sometimes even lose your vision partially or completely. A timely visit to the doctor when the first suspicious symptoms appear will help protect against complications. The main thing is to follow the ophthalmologist’s treatment recommendations after the infection has been accurately diagnosed!
Symptoms and consequences of the disease
Depending on the causes of its appearance, the disease can develop within a few hours and occur in acute or chronic form. Knowing the symptoms of keratitis development, the owner will be able to seek help from a veterinarian in time. With keratitis in a cat, the following is observed:
- inflammation of the eyelids (blepharitis); — intolerance to sunlight and artificial light (photophobia); - squinting of the affected eye (blepharospasm); - accumulation of infiltrate inside the cornea (fluid), causing the eye to swell; — clouding of the cornea (it becomes matte, in contrast to a healthy shiny one); - the appearance of blood vessels on the cornea; - discharge from the inflamed eye and pus in the corners (the fur under the eye will be damp).
The animal also develops itching, which causes it to scratch the eye with its paws, which leads to inflammation of the eyelids. If treatment for keratitis in a cat or kitten is started late or performed incorrectly, this can lead to the following consequences:
- the appearance of a thorn (a cloudy spot on the eye); - development of cataracts or glaucoma; - corneal breakthrough; - the appearance of scars (in this case, further treatment is useless, the moment is missed - the cat will go blind).
Our services in ophthalmology:
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with an ophthalmologist (primary) | 3 900 |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (repeated, for complex programs) within 3 months after the initial one | 2 000 |
| Ultrasound scanning of the anterior segment of the eye | 1 000 |
| Removal of foreign bodies of the cornea, conjunctiva | 2 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Forms and types of keratitis
Keratitis in cats has several forms:
1. Viral. Most often caused by an adenovirus or herpes virus. When it occurs, the integrity of the cornea is compromised, and as the disease develops, deeper layers are also affected.
Read more about herpes: Treatment of herpes in cats
2. Allergic. Develops as a result of improper administration of medications or an allergy to a vaccine. It causes redness, tearing and swelling.
3. Bacterial. Develops due to bacteria entering the organ of vision after injury. It occurs acutely, with severe purulent complications.
4. Neurogenic, or ulcerative. It is caused by damage to nervous tissue as a result of diabetes mellitus, chronic renal failure, and hypovitaminosis. With this form, ulcers appear in the cat's eye, but she does not experience pain. The disease goes away on its own if there is no secondary infection.
5. Eosinophilic. Occurs when blood enters the cornea. Most often, this form becomes chronic. Frequent relapses are possible.
The disease also varies in severity:
— purulent superficial (inflammation of the upper layer of the cornea); — deep purulent (inflammation of all layers of the cornea); - vascular superficial (capillaries grow into the upper layer of the cornea).
Risk factors
The causes of keratitis are known, and there are also risk factors that significantly increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
Immediate causes include:
- Infections, parasitic infestations.
- Mechanical injuries, chemical, thermal damage.
- Allergy.
These causes lead to the occurrence of infectious (for example, herpetic), traumatic or allergic keratitis, respectively.
Among the risk factors for developing the disease, the following are most important:
- Presence of autoimmune diseases.
- Long-term wearing of contact lenses.
- Dry eye syndrome.
- Lack of vitamins.
- Various metabolic disorders.
- The presence of some systemic diseases: diabetes, gout, rheumatism.
Based on the list of risk factors, it is clear that keratitis is a fairly common pathology.
Treatment of keratitis in adults
American actress Deborah Edwards once said: “The only people who don’t like cats are those who haven’t met their cat yet.” It is impossible not to love furry friends, as well as to watch their poor health with peace of mind. However, when treating keratitis in a cat, the owner must keep in mind that the cause of the disease is eliminated in the first place. Antimicrobial and hormonal drugs, of course, will work, but, with a greater degree of probability, keratitis will return. We at Murkosh categorically do not recommend self-medication - there is a risk of harming your pet.
Treatment of keratitis requires an integrated approach. So, for fungal, bacterial and viral forms, antifungal and antibacterial drugs are prescribed, respectively. And also interferon-containing. In case of complications, sulfonamide drugs and antibiotics are prescribed. For ulcerative and purulent cases, eye drops and antiseptics are instilled into the conjunctival sac. The animal is prescribed antibiotics, and if ulcers or neoplasms are found, eye microsurgery is performed. Using an antiseptic solution helps a lot:
— 3% boric acid; - 1% rivanol; - furatsilin in a ratio of 1:5000.
The eosinophilic form of keratitis in cats requires immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory drugs. The following may also be prescribed:
1. "Dekta-2". Eye drops for the treatment of keratitis, blepharitis, allergic conjunctivitis. The cost is about 170 rubles for 5 ml.
2. "Bars". Eye drops with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and anesthetic properties. They are used to treat acute and chronic forms of conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, and injuries to the organs of vision. The cost is about 200 rubles for 10 ml.
3. "Ophthalmosan". Eye drops for the prevention and treatment of keratitis, blepharitis, allergic conjunctivitis and other bacterial diseases. The cost is about 250 rubles for 15 ml.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of herpetic keratitis begins with examination. The presence of characteristic blisters suggests a lesion caused by herpes. Since the disease can be sluggish, without characteristic manifestations, the diagnosis is clarified using laboratory and instrumental studies. To detect the pathogen, scrapings are taken from the affected tissues or tear fluid.
Laboratory diagnosis of ophthalmoherpes includes:
- Study of scrapings from the conjunctiva using fluorescent antibodies.
- Linked immunosorbent assay.
- Blood or tear fluid test for antiherpetic antibodies.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of biological fluids that detects the virus.
Instrumental examination helps to assess the extent and depth of anatomical changes. Instrumental diagnostics include anterior optical coherence tomography, biomicroscopy and fluorescein test.
A fluorescein test is performed to identify ulcers or films on the cornea and assess the area and extent of the lesion. After applying the solution to the eye, the ophthalmologist examines the tissue using a slit lamp with a blue filter.
Preventive measures
It is better to prevent any disease than to treat it. Keratitis in cats is no exception. To prevent illness in pets:
— Keep the house clean, wipe off the dust. — The animal’s diet must be balanced. The best choice is professional super-premium and holistic-class food. — “Murkoshi” volunteers recommend getting vaccinated in a timely manner. Vaccinations will help protect your pet's body from infection. - Brush the cat. Lost hair can get into the eye, rub the cornea and conjunctiva, leading to inflammation. — Do not keep open chemicals within the cat’s reach to avoid burns. — Strengthen your animal’s immunity with vitamins. Remember to deworm.
Read more about deworming: Preparations for deworming cats
— Examine your pet’s eyes, especially if there is watery eyes. Mechanical irritation of the cornea is possible. — If the animal has a predisposition to keratitis, eye examinations should be performed more often.
The danger of keratitis for a kitten or cat cannot be underestimated. But, at the same time, it is possible to cure the disease by noticing deviations in the animal’s well-being and unhealthy eye conditions in time and contacting a veterinarian.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture of keratitis is a series of manifestations specific to this disease, which have received a special name - corneal syndrome.
It includes symptoms:
- increased lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- narrowing of the palpebral fissure, it is impossible to open the eye completely;
- eye pain;
- sensation of a foreign object in the eye;
- redness of the eye.
In severe cases, the inflammatory process spreads to other parts of the eye and affects the sclera and iris. Another possible complication is ulceration at the site of inflammation. It can lead to perforation, in which infection enters the deep structures of the eye.